What is NAS?
An NAS device is a storage device connected to a network that allows storage and retrieval of data from a central location for authorized network users and varied clients. NAS devices are flexible and scale out, meaning that as you need additional storage, you can add to what you have. NAS is like having a private cloud in the office. It’s faster, less expensive and provides all the benefits of a public cloud on site, giving you complete control.
With a NAS, data is continually accessible, making it easy for employees to collaborate, respond to customers in a timely fashion, and promptly follow up on sales or other issues because information is in one place. Because NAS is like a private cloud, data may be accessed remotely using a network connection, meaning employees can work anywhere, anytime.


NAS systems are perfect for SMBs.
- Simple to operate, a dedicated IT professional is often not required
- Lower cost
- Easy data backup, so it’s always accessible when you need it
- Good at centralizing data storage in a safe, reliable way
Scattered storage arrangements will not work for SMBs.
- Out-of-sync data
- Reliability and accessibility issues if storage goes down
- Delays in responding to customer service requests or sales queries
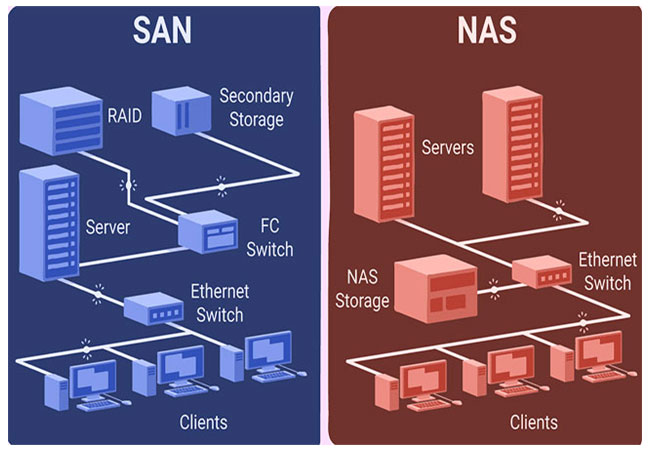
SAN vs. NAS
Both SAN and network-attached storage (NAS) are methods of managing storage centrally and sharing that storage with multiple hosts (servers). However, NAS is Ethernet-based, while SAN can use Ethernet and Fibre Channel. In addition, while SAN focuses on high performance and low latency, NAS focuses on ease of use, manageability, scalability, and lower total cost of ownership (TCO). Unlike SAN, NAS storage controllers partition the storage and then own the file system. Effectively this makes a NAS server look like a Windows or UNIX/Linux server to the server consuming the storage.

NAS Protocols:
- Common Internet File Services / Server Message Block (CIFS/SMB). This is the protocol that Windows usually uses
- Network File System (NFS). NFS was first developed for use with UNIX servers and is also a common Linux protocol
